Suhosin (pronounced ‘su-ho-shin’) is an advanced protection system for PHP 5 installations. It is designed to protect servers and users from known and unknown flaws in PHP applications and the PHP core. Suhosin comes in two independent parts, that can be used separately or in combination. The first part is a small patch against the PHP core, that implements a few low-level protections against buffer overflows or format string vulnerabilities and the second part is a powerful PHP extension that implements numerous other protections.
In this tutorial we will show you how to install Suhosin PHP 5 protection security patch on CentOS.
Install Suhosin PHP 5 Protection Security Patch on CentOS
Step 1. First let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
yum clean all yum -y update
Step 2. Download latest version of Suhosin:
#yum install php-devel #http://download.suhosin.org/suhosin-0.9.35.tgz #tar -xvf suhosin-0.9.35.tgz
Next, run the following commands to compile Suhosin under PHP 5:
#cd suhosin-0.9.33 #phpize #./configure #make #make install
Create the suhosin configuration, type the following command:
#echo 'extension=suhosin.so' > /etc/php.d/suhosin.ini
Restart web server Nginx, Lighttpd or Apache:
#service nginx restart #service lighttpd restart #service httpd restart
Step 3. Verify Suhosin installation
#php -v
Suhosin should now be installed. You can check by creating a file called info.php in /var/www/html/ with the following content:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
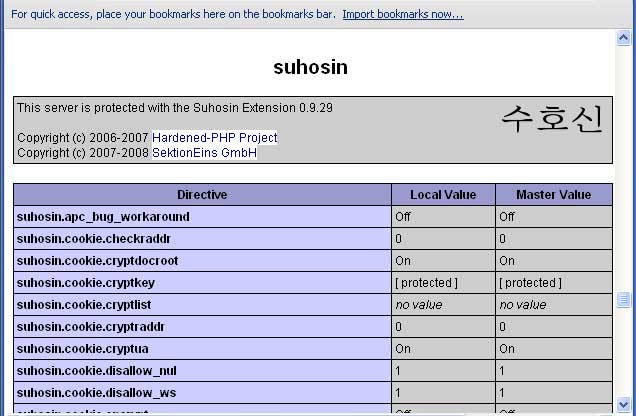
The features of the Suhosin patch are listed under Engine Protection (only with patch); all the other features come with the Suhosin extension. But if you would like configure it according to your setup, then visit the suhosin configuration page for more information.