Elefant is a refreshingly simple PHP content management system and web framework. Elefant is easy-to-use and straight-forward for all levels of users. Elefant is also secure, extremely fast, well-documented, and well-tested, making it an ideal platform for web developers to build on for their own custom web applications. Continue reading “How To Install Elefant CMS on Ubuntu 16.04”
How To Install WikkaWiki on Ubuntu 16.04
WikkaWiki (aka Wikka) is a flexible, standards-compliant and lightweight wiki engine written in PHP, which uses MySQL to store pages. Forked from WakkaWiki. Designed for speed, extensibility, and security. Released under the GPL license. Continue reading “How To Install WikkaWiki on Ubuntu 16.04”
How To Install Google Chrome on Ubuntu 16.04
Google Chrome is a freeware web browser developed by Google, uses the WebKit layout engine. It is available for the Linux, Android, iOS, Microsoft Windows, and Mac OS X operating systems. But Google Chrome is more than a web browser, as it combines sophisticated open source technology, borrowed from the Chromium application, into a minimal design, all in order to help users surf the web much faster, a lot easier, and safer than ever before. Continue reading “How To Install Google Chrome on Ubuntu 16.04”
How To Install Joomla on Ubuntu 16.04
Joomla is a free and open source popular content management that uses a PHP and a backend database, such as MySQL. It offers a wide variety of features that make it an incredibly flexible content management system right out of the box. Furthermore, there are hundreds of free extensions written for that allows users to extend its functionality and customize it to their own objectives. A major advantage of using a content management system (CMS) is that it requires almost no technical skill or knowledge to manage. if you are planning to publish content on your website frequently, then maybe using WordPress will be a better option for you.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple. I will show you through the step by step installation Joomla in Ubuntu 16.04 server.
Install Joomla on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 16.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php7.0-mysql php7.0-curl php7.0-json php7.0-cgi php7.0 libapache2-mod-php7.0 <code>php7.0-mcrypt </code>
Step 3. Installing Joomla.
First thing to do is to go to Joomla’s download page and download the latest stable version of Joomla, At the moment of writing this article it is version 3.5.1:
wget https://github.com/joomla/joomla-cms/releases/download/3.5.1/Joomla_3.5.1-Stable-Full_Package.zip mkdir /var/www/html/joomla unzip Joomla_3.5.1-Stable-Full_Package.zip -d /var/www/html/
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data.www-data /var/www/html chmod -R 755 /var/www/html
By default, Apache2, installed a test html page in the /var/www/html directory called index.html. Remove that page if you want to. Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for Joomla.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB.
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Joomla. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Joomla installation:
CREATE DATABASE joomladb;
CREATE USER joomlauser@localhost;
SET PASSWORD FOR 'joomlauser'@'localhost' = PASSWORD("your-password");
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON joomladb.* TO 'joomlauser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-password' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit
Step 5. Configuring Apache web server for Joomla.
Create a new virtual host directive in Apache. For example, create a new Apache configuration file named ‘joomla.conf’ on your virtual server:
sudo a2enmod rewrite touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/joomla.conf nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf
Add the following lines:
ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot /var/www/html/ ServerName your-domain.com ServerAlias www.your-domain.com Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny allow from all ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-error_log CustomLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-access_log common
Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 6. Accessing Joomla.
Joomla will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com/ or http://server-ip and complete the required the steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
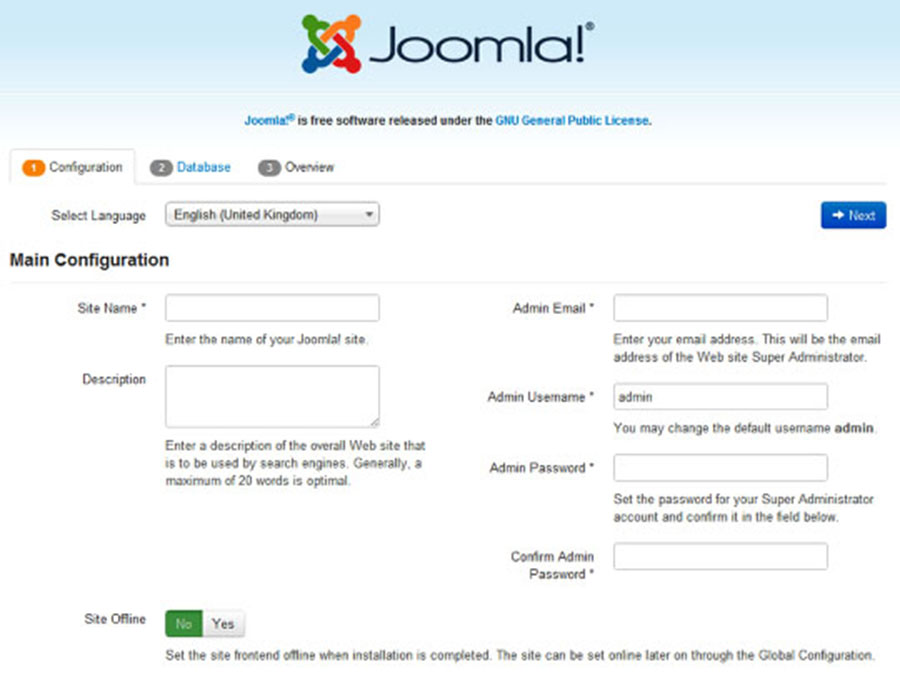
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Joomla. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Joomla CMS (content management system) on Ubuntu 16.04 systems. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Joomla web site.
You Might Also Like: How To Install WordPress with Docker on Ubuntu 16.04
How To Install Webmin on Ubuntu 16.04
Webmin is a free control Panel for managing VPS. Webmin is a web based interface which is used to manage VPS web hosting server. With the help of webmin you can setup user account, apache, dns and file sharing and other actions. Webmin very suitable for beginners who do not know much about the unix or linux command line.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Webmin on a Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) server.
Install Webmin on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First you need add Webmin official repository and make sure that all packages are up to date.
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
And add the following lines:
deb http://download.webmin.com/download/repository sarge contrib deb http://webmin.mirror.somersettechsolutions.co.uk/repository sarge contrib
Fetch and install the GPG key:
sudo wget http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.asc sudo apt-key add jcameron-key.asc
Step 2. Installing Webmin.
Install Webmin with the following command:
apt-get update apt-get install webmin -y
Now, allow the Webmin default port via a firewall:
sudo ufw allow 10000
Step 3. Access Webmin.
Finaly, we can access the webmin panel using our web browser. Webmin use 10000 as its default port. Type this into our URL address web browser. https://ip-address:10000 then login as super user or root access priviliges. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 and 10000 to enable access to the control panel.
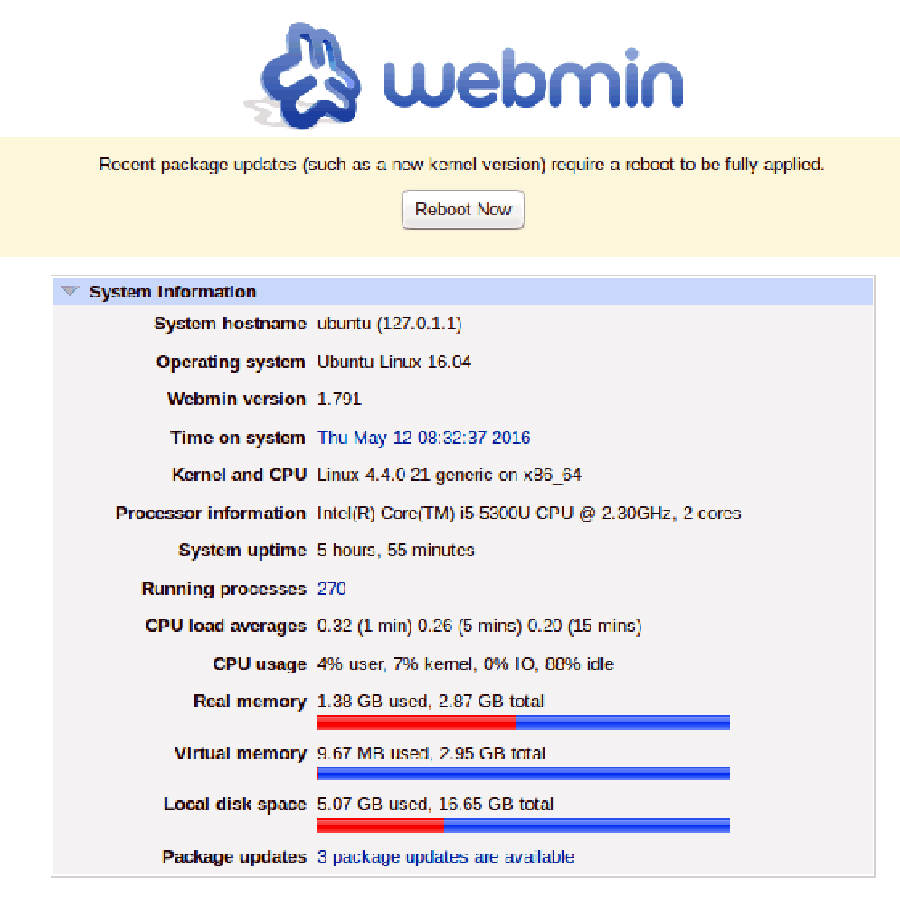
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Webmin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Webmin control panel in Ubuntu 16.04 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Webmin web site.
You Might Also Like: How To Install Webmin on CentOS
How to Install Cinnamon on Ubuntu 16.04
Cinnamon is an open source project that provides users with a full featured desktop environment for GNU/Linux operating systems. It is a fork of the GNOME Shell user interface distributed with the GNOME project. It has been designed from the ground up to provide users with a traditional, yet advanced and modern graphical session for their Linux-based operating systems. It’s usually deployed on the Linux Mint distribution.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Cinnamon on a Ubuntu 16.04 server.
Install Cinnamon on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Installing Cinnamon.
First add the community PPA and this PPA can be used only by Xenial users. And please make sure that idr00t doesn’t provide any guarantee and you understand that you install at your own risk. But the following community PPA has been un-officially given the go ahead by Moorkai, one of the developers behind the popular Cinnamon PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:embrosyn/cinnamon
Now, type the following command to finally install Cinnamon:
sudo apt-get install cinnamon
To check the installed version of Cinnamon, please issue the below command on your terminal to check whether Cinnamon is installed or not:
cinnamon --version
Step 3. Accessing Cinnamon.
If everything goes OK, log out and select log in with Cinnamon session or Cinnamon (Software Rendering) session if you want it use software rendering to do more of the graphical work):
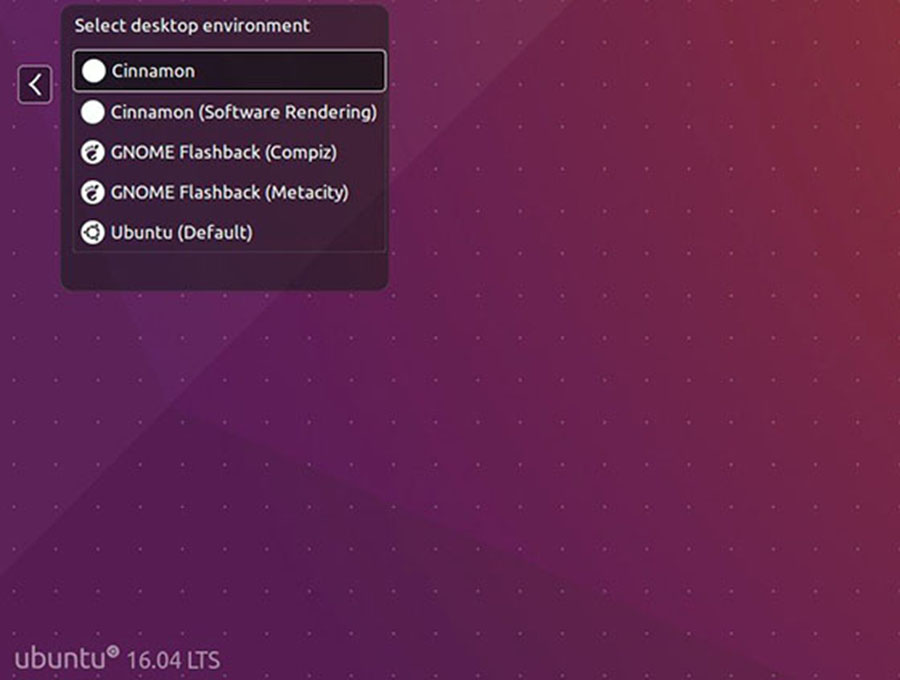
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Cinnamon. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Cinnamon on your Ubuntu 16.04 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Cinnamon web site.
How To Install MongoDB on Ubuntu 16.04
MongoDB is a NoSQL document-oriented database. Refers to a database with a data model other than the tabular format used in relational databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL. MongoDB features include: full index support, replication, high availability, and auto-sharding. It is a cross-platform and it makes the process of data integration faster and much easier. Since it is free and open-source, MongoDB is used by number of websites and organizations.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation MongoDB on a Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) server.
Install MongoDB on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install MongoDB packages.
First to completely remove an existing Mongodb from your machine if you have that in already:
sudo apt-get remove mongodb sudo apt-get autoremove
A stable version of MongoDB packages are already in the default Ubuntu repository. However, the version in Ubuntu’s repository isn’t the latest. If you want to install the latest version you must add a third-party repository to your system and install it from there:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv EA312927
Next, run the commands below to add trusty repository:
echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu trusty/mongodb-org/3.2 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.2.list
After that, update your system and refresh existing repositories by running the commands below:
sudo apt-get update
And now install the latest stable version of MongoDB:
apt-get install -y --allow-unauthenticated mongodb-org
Step 3. Verifying MongoDB database.
To verify it is successfully installed, run the commands below to view its running status:
# sudo service mongodb enable
# sudo service mongodb start
# sudo service mongodb status
● mongodb.service - LSB: An object/document-oriented database
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/mongodb; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2016-06-4 16:40:35 IST; 14s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 2849 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/mongodb start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 1593 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 13 (limit: 512)
Memory: 51.9M
CPU: 100ms
CGroup: /system.slice/mongodb.service
└─2861 /usr/bin/mongod --config /etc/mongodb.conf
A good way to start using MongoDB on your Ubuntu 16.04 is to read the MongoDB manual on the official web site.
https://docs.mongodb.org/manual/
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed MongoDB. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing MongoDB in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official MongoDB web site.
You Might Also Like: How To Install MongoDB on CentOS 6






