PrestaShop is an open-source e-commerce solution which allows you to maintain your own online shop. It PrestaShop is 100% free. This software is published under the Open Software License (OSL). It is written in PHP programming language with support for the MySQL database management system. More than 250,000 ecommerce sites run on PrestaShop. It supports many different payment gateway systems like PayPal, Google Checkout etc etc. Continue reading “How To Install PrestaShop on Ubuntu 16.04”
How To Install Elefant CMS on Ubuntu 16.04
Elefant is a refreshingly simple PHP content management system and web framework. Elefant is easy-to-use and straight-forward for all levels of users. Elefant is also secure, extremely fast, well-documented, and well-tested, making it an ideal platform for web developers to build on for their own custom web applications. Continue reading “How To Install Elefant CMS on Ubuntu 16.04”
How To Install WikkaWiki on Ubuntu 16.04
WikkaWiki (aka Wikka) is a flexible, standards-compliant and lightweight wiki engine written in PHP, which uses MySQL to store pages. Forked from WakkaWiki. Designed for speed, extensibility, and security. Released under the GPL license. Continue reading “How To Install WikkaWiki on Ubuntu 16.04”
How To Install Joomla on Ubuntu 16.04
Joomla is a free and open source popular content management that uses a PHP and a backend database, such as MySQL. It offers a wide variety of features that make it an incredibly flexible content management system right out of the box. Furthermore, there are hundreds of free extensions written for that allows users to extend its functionality and customize it to their own objectives. A major advantage of using a content management system (CMS) is that it requires almost no technical skill or knowledge to manage. if you are planning to publish content on your website frequently, then maybe using WordPress will be a better option for you.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple. I will show you through the step by step installation Joomla in Ubuntu 16.04 server.
Install Joomla on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 16.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php7.0-mysql php7.0-curl php7.0-json php7.0-cgi php7.0 libapache2-mod-php7.0 <code>php7.0-mcrypt </code>
Step 3. Installing Joomla.
First thing to do is to go to Joomla’s download page and download the latest stable version of Joomla, At the moment of writing this article it is version 3.5.1:
wget https://github.com/joomla/joomla-cms/releases/download/3.5.1/Joomla_3.5.1-Stable-Full_Package.zip mkdir /var/www/html/joomla unzip Joomla_3.5.1-Stable-Full_Package.zip -d /var/www/html/
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data.www-data /var/www/html chmod -R 755 /var/www/html
By default, Apache2, installed a test html page in the /var/www/html directory called index.html. Remove that page if you want to. Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for Joomla.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB.
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Joomla. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Joomla installation:
CREATE DATABASE joomladb;
CREATE USER joomlauser@localhost;
SET PASSWORD FOR 'joomlauser'@'localhost' = PASSWORD("your-password");
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON joomladb.* TO 'joomlauser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-password' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit
Step 5. Configuring Apache web server for Joomla.
Create a new virtual host directive in Apache. For example, create a new Apache configuration file named ‘joomla.conf’ on your virtual server:
sudo a2enmod rewrite touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/joomla.conf nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf
Add the following lines:
ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot /var/www/html/ ServerName your-domain.com ServerAlias www.your-domain.com Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny allow from all ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-error_log CustomLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-access_log common
Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 6. Accessing Joomla.
Joomla will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com/ or http://server-ip and complete the required the steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
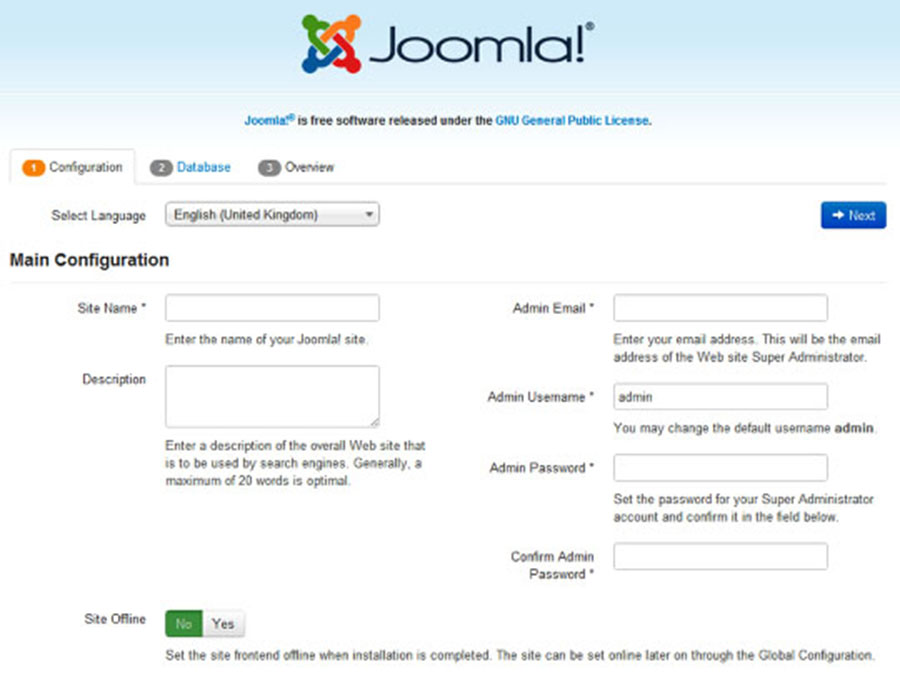
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Joomla. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Joomla CMS (content management system) on Ubuntu 16.04 systems. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Joomla web site.
You Might Also Like: How To Install WordPress with Docker on Ubuntu 16.04
How To Install Textpattern on Ubuntu 16.04
Textpattern is an elegant CMS. It is a free open source software that allows web developers, designers, and bloggers to publish their content within a clean and easy interface. Texpattern comes with full range of features and it allows you to easily create, edit and publish content on your website.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Textpattern on a Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) server.
Install Textpattern on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 16.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php5 php5-mysql php5-gd php5-curl libssh2-php
Step 3. Installing Textpattern.
First thing to do is to go to Textpattern’s download page and download the latest stable version of Textpattern, At the moment of writing this article it is version 4.5.7:
wget https://textpattern.com/file_download/75/textpattern-4.6.2.zip unzip Textpattern-4.6.2.zip -d /var/www/html cd textpattern-4.6.2 cp -a * ..
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/ [/hp] <strong>Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for Textpattern.</strong> By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB. [php] mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Textpattern. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Textpattern installation:
CREATE DATABASE textpattern; CREATE USER 'Ttextpatternuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `textpattern`.* TO 'textpatternuser'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Step 5. Configuring Apache web server for Textpattern.
Create a new virtual host directive in Apache. For example, create a new Apache configuration file named ‘textpattern.conf’ on your virtual server:
sudo a2enmod rewrite touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/textpattern.conf ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/textpattern.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/textpattern.conf nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/textpattern.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/" ServerName your-domain.com ServerAlias www.your-domain.com <Directory "/var/www/html/"> Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny allow from all </Directory> ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-error_log CustomLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-access_log common </VirtualHost>
Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 6. Accessing Textpattern.
Textpattern will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com/setup/index.php or http://server-ip/setup/index.php and complete the required the steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Textpattern. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Textpattern content management system (CMS) on yourUbuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Textpattern web site.
How To Install Shopware on Ubuntu 16.04
Shopware is the next generation of open source e-commerce software made in Germany. Based on bleeding edge technologies like Symfony 2, Doctrine 2 and Zend Framework Shopware comes as the perfect platform for your next e-commerce project. Furthermore Shopware provides an event-driven plugin system and an advanced hook system, giving you the ability to customize every part of the platform.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Shopware on a Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) server.
Install Shopware on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 16.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php5 php5-mysql php5-gd php5-curl libssh2-php
Step 3. Installing Shopware.
First thing to do is to go to Shopware’s download page and download the latest stable version of Shopware, At the moment of writing this article it is version 5:
wget https://github.com/shopware/shopware/archive/v5.1.6.zip unzip v5.1.6.zip -d /var/www/html cd /var/www/html/shopware-5.1.6 cp -a * ..
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for Shopware.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB.
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Shopware. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Shopware installation:
CREATE DATABASE shopware; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON shopware.* TO 'shopware'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'strong_password'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; \q
Step 5. Configuring Apache web server for Shopware.
Create a new virtual host directive in Apache. For example, create a new Apache configuration file named ‘shopware.conf’ on your virtual server:
sudo a2enmod rewrite touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/shopware.conf ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/shopware.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/shopware.conf nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/shopware.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/" ServerName your-domain.com ServerAlias www.your-domain.com <Directory "/var/www/html/"> Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny allow from all </Directory> ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-error_log CustomLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-access_log common </VirtualHost>
Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 6. Accessing Shopware.
Shopware will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com or http://server-ip and complete the required the steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Shopware. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Shopware open source e-commerce on your Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Shopware web site.
How To Install MariaDB on Ubuntu 16.04
MariaDB is a an open source and cross-platform database engine and server, designed as a drop-in replacement for the well known and powerful MySQL database engine used on numerous web servers around the world. The application is geared toward database professionals that are in search of a scalable, robust, reliable and stable SQL server, a replacement for the MySQL database server.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple. I will show you through the step by step installation MariaDB on 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) server.
Install MariaDB on Ubuntu 16.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
apt-get update apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Installing MariaDB.
Installing MariaDB is as simple as running just one command below:
apt-get install mariadb-server
If you want to install MariaDB 10.x Which is not included in distribution repository. We going to add MariaDB repo to our system:
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xF1656F24C74CD1D8 sudo add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64,i386,ppc64el] http://ftp.utexas.edu/mariadb/repo/10.1/ubuntu xenial main
Once the key is imported and the repository added you can install MariaDB with:
apt-get update apt-get install mariadb-server
Once complete, you can verify MariaDB is installed by running the below command:
systemctl start mariadb systemctl status mariadb
Step 3. Securing MariaDB after installation.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
To log into MariaDB, use the following command (note that it’s the same command you would use to log into a MySQL database):
mysql -u root -p
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed MariaDB. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing MariaDB in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official MariaDB web site.






