Joomla is a free and open source popular content management that uses a PHP and a backend database, such as MySQL. It offers a wide variety of features that make it an incredibly flexible content management system right out of the box. Furthermore, there are hundreds of free extensions written for that allows users to extend its functionality and customize it to their own objectives. A major advantage of using a content management system (CMS) is that it requires almost no technical skill or knowledge to manage. if you are planning to publish content on your website frequently, then maybe using WordPress will be a better option for you.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Joomla with Nginx on an Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver) server.
Install Joomla With Nginx on Ubuntu 18.04
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LEMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 18.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php7.1-cli php7.1-gd php7.1-opcache php7.1-mysql php7.1-json php7.1-mcrypt php7.1-xml php7.1-curl
Step 3. Installing Joomla with Nginx on Ubuntu 18.04.
First thing to do is to go to Joomla’s download page and download the latest stable version of Joomla, At the moment of writing this article it is version 3.8.5:
wget https://downloads.joomla.org/us/cms/joomla3/3-8-12/Joomla_3-8-12-Stable-Full_Package.zip mkdir /var/www/html/joomla unzip Joomla*.zip -d /var/www/html/joomla
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data.www-data /var/www/html chmod -R 755 /var/www/html
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for Joomla.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB.
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Joomla. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Joomla installation:
CREATE DATABASE joomladb;
CREATE USER joomlauser@localhost;
SET PASSWORD FOR 'joomlauser'@'localhost' = PASSWORD("your-password");
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON joomladb.* TO 'joomlauser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-password' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit
Step 5. Configuring Nginx web server for Joomla.
Finally, configure Nginx site configuration file for Joomla. Run the commands below to create a new configuration file called joomla:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/joomla
Add the following lines:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
root /var/www/html/joomla;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.1-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
After configuring the VirtualHost above, enable it by running the commands below:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/joomla /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Now, we can restart Apache web server so that the changes take place:
nginx -t systemctl restart nginx systemctl restart php7.1-fpm
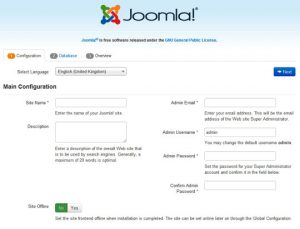
Step 6. Accessing Joomla.
Joomla will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com/ or http://server-ip and complete the required the steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=prBpxVspDHs]
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Joomla. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Joomla CMS (content management system) with Nginx on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS systems. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Joomla web site.