Seafile is a open source cloud storage software. It offers file sharing and syncing for individual users and groups, it provides client side encryption and easy access from mobile devices. Also easily integrated with local services such as LDAP and WebDAV or can be deployed using advanced network services and databases like MySQL, SQLite, PostgreSQL, Memcached, Nginx or Apache Web Server.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Seafile open source secure cloud storage on a Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) server.
Install Seafile on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial Xerus
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running these following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LEMP (Linux, Nginx, MariaDB, PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 16.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LEMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php7.0-curl php7.0-gd php7.0-mbstring php7.0-mysql libapache2-mod-php7.0 php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-zip
Installing Python modules:
apt-get install python2.7 libpython2.7 python-setuptools python-imaging python-ldap python-mysqldb python-memcache python-urllib3
Step 3. Configure the MariaDB database for Seafile.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each steps carefully which will set root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB.
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Seafile. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Seafile installation:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database ccnet_db character set = 'utf8'; MariaDB [(none)]> create database seafile_db character set = 'utf8'; MariaDB [(none)]> create database seahub_db character set = 'utf8'; MariaDB [(none)]> create user seacloud@localhost identified by 'password'; MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on ccnet_db.* to seacloud@localhost identified by 'password'; MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on seafile_db.* to seacloud@localhost identified by 'password'; MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on seahub_db.* to seacloud@localhost identified by 'password'; MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; MariaDB [(none)]> exit
Step 4. Installing Seafile on Server.
You need to download the last stable release of Seafile:
wget https://bintray.com/artifact/download/seafile-org/seafile/seafile-server_6.0.6_x86-64.tar.gz
Extract the tarball into the current directory:
tar -xvzf seafile-server_6.0.6_x86-64.tar.gz mv seafile-server_6.0.6 seafile-server
Install Seafile:
Run this script which will create the required databases and directories for the Seafile server and and answer all questions using the following configuration options, after the script verifies the existence of all Python required modules:
./setup-seafile-mysql.sh
After Seafile server successfully installs, it will generate some useful information such as what ports needs to be open on your Firewall to allow external connection and what scripts to handle in order to start the server.
Step 5. Starting the Seafile services.
Create startup script for the Seafile server like this:
nano /lib/systemd/system/seafile.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit] Description=Seafile Server After=network.target mariadb.service[Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/home/seafile/seafile-server/seafile.sh start ExecStop=/home/seafile/seafile-server/seafile.sh stop RemainAfterExit=yes User=seafile Group=seafile[Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save the file and create a new service file for seahub:
[Unit] Description=Seafile Hub After=network.target seafile.target[Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/home/seafile/seafile-server/seahub.sh start-fastcgi ExecStop=/home/seafile/seafile-server/seahub.sh stop RemainAfterExit=yes User=seafile Group=seafile[Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Now try using the service and command to start a new Seafile server instance:
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start seafile systemctl start seahub
Step 6. Configuring Nginx web server for Seafile.
*Note: A static IP address 192.168.77.21 configure on your server.
First, create a new virtual host file with name seafile.conf:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile.conf
Add the following lines:
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.77.21;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;# Reverse proxy for seafile
location / {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_script_name;fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol;
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length;
fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr;access_log /var/log/nginx/seahub.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/seahub.error.log;
fastcgi_read_timeout 36000;
}# Reverse Proxy for seahub
location /seafhttp {
rewrite ^/seafhttp(.*)$ $1 break;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082;
client_max_body_size 0;
proxy_connect_timeout 36000s;
proxy_read_timeout 36000s;
proxy_send_timeout 36000s;
send_timeout 36000s;
}#CHANGE THIS PATH WITH YOUR OWN DIRECTORY
location /media {
root /home/seafile/seafile-server/seahub;
}
}
Save the file and restart nginx:
systemctl restart nginx
Step 7. Accessing Seafile.
Seafile cloud storage will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com or http://192.168.77.21. Enter the admin email id and password to login which you have created at the time of installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 8000 to enable access to the control panel.
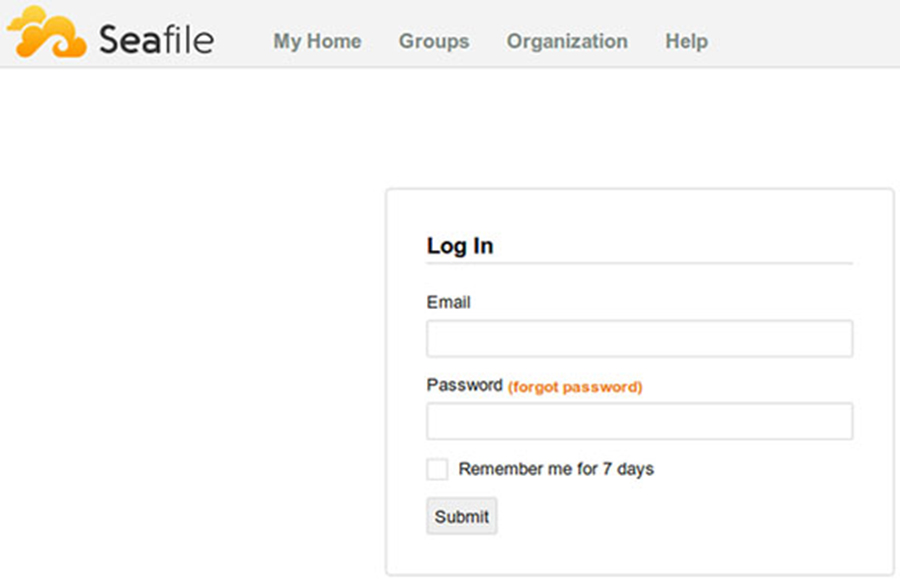
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Seafile. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Seafile open source secure cloud storage on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Seafile web site.