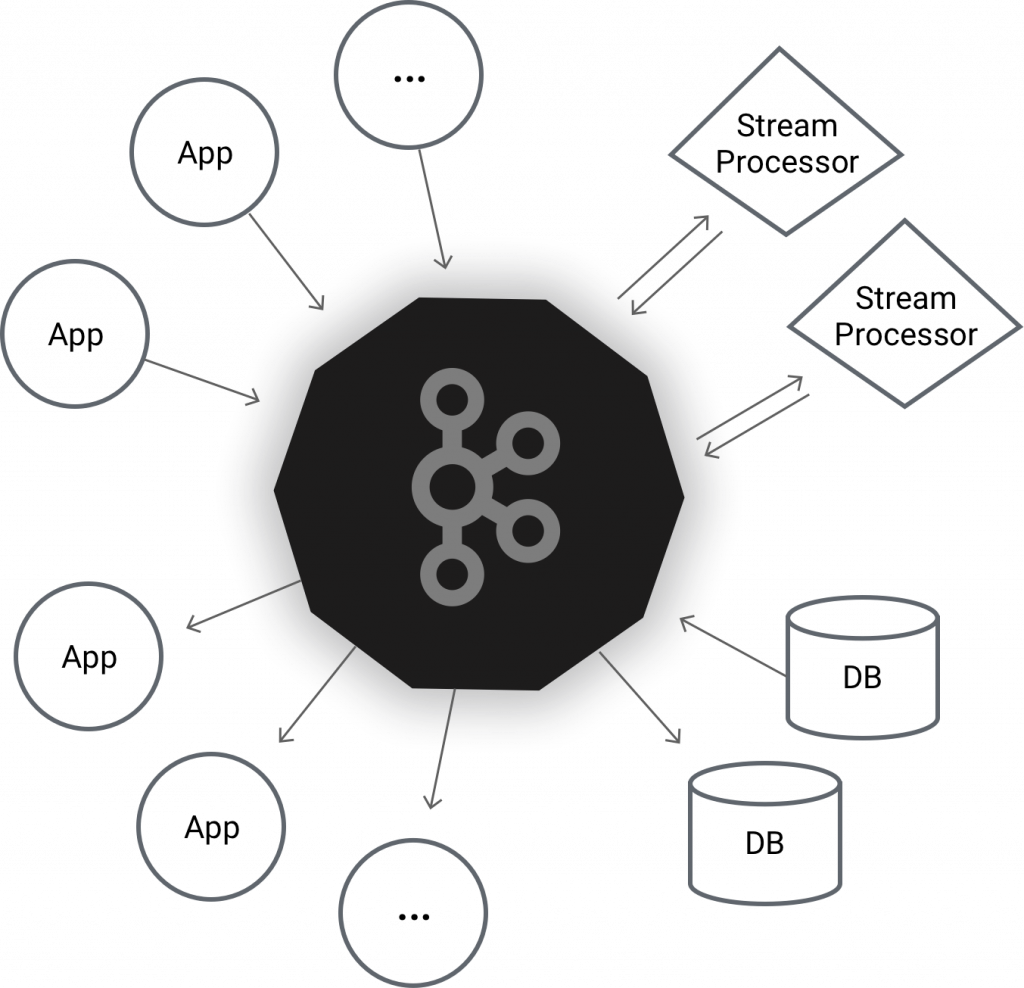
Apache Kafka is a distributed message agent designed to deal with huge volumes of real time information effectively. Unlike traditional agents like ActiveMQ and RabbitMQ, Kafka functions as a bunch of one or more servers that makes it highly scalable and because of the distributed nature, it’s inbuilt fault-tolerance whilst providing greater throughput when compared to its counterparts.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation Apache Kafka on a 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) server.
Install Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
Step 1. First make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Installing Java.
Apache Spark requires Java to be installed on your server. By default, Java is not available in Ubuntu’s repository. Add the Oracle Java PPA to Apt with the following command:
add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java apt-get update -y apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
Verify the Java version by running the following command:
java -version
Step 3. Installing Zookeeper.
Apache Kafka depends on Zookeeper for cluster management. Hence, prior to starting Kafka, Zookeeper has to be started:
apt-get install zookeeperd
After the installation completes, ZooKeeper will be started as a daemon automatically. By default, it will listen on port 2181:
netstat -ant | grep :2181
You can run the following command to check whether zookeeper is running:
systemctl status zookeeper
Step 4. Download and Installing Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
First, download and extract Kafka from Apache website. You can use wget to download Kafka:
wget http://www-us.apache.org/dist/kafka/1.1.0/kafka_2.12-1.1.0.tgz
Then extract the archive file:
tar xzf kafka_2.12-1.1.0.tgz mv kafka_2.12-1.1.0 /usr/local/kafka
Start Kafka Server:
cd /usr/local/kafka bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
Now start the Kafka server:
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties ... [2018-06-26 10:59:45,989] INFO Kafka version : 1.0.1 (org.apache.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser) [2018-06-26 10:59:45,995] INFO Kafka commitId : c0518aa65f25317e (org.apache.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser) [2018-06-26 10:59:46,006] INFO [KafkaServer id=0] started (kafka.server.KafkaServer)
Step 5. Create a Topic on Kafka.
Let’s create a topic named “NewTopic” with a single partition and only one replica:
bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic NewTopic Created topic "NewTopic".
Now you can see the created topic on Kafka by running the list topic command:
bin/kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper localhost:2181 NewTopic
Step 6. Send Messages to Kafka.
The “producer” is the process responsible for put data into our Kafka. The Kafka comes with a command line client that will take input from a file or from standard input and send it out as messages to the Kafka cluster:
Let’s run the producer and then type a few messages into the console to send to the server:
bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic NewTopic >Welcome to kafka >This is my new topic >
Step 7. Using Kafka Consumer.
Kafka also has a command line consumer to read data from Kafka cluster and display messages to standard output:
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic NewTopic --from-beginning Welcome to kafka This is my new topic
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Apache Kafka. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Apache Kafka Documentation.