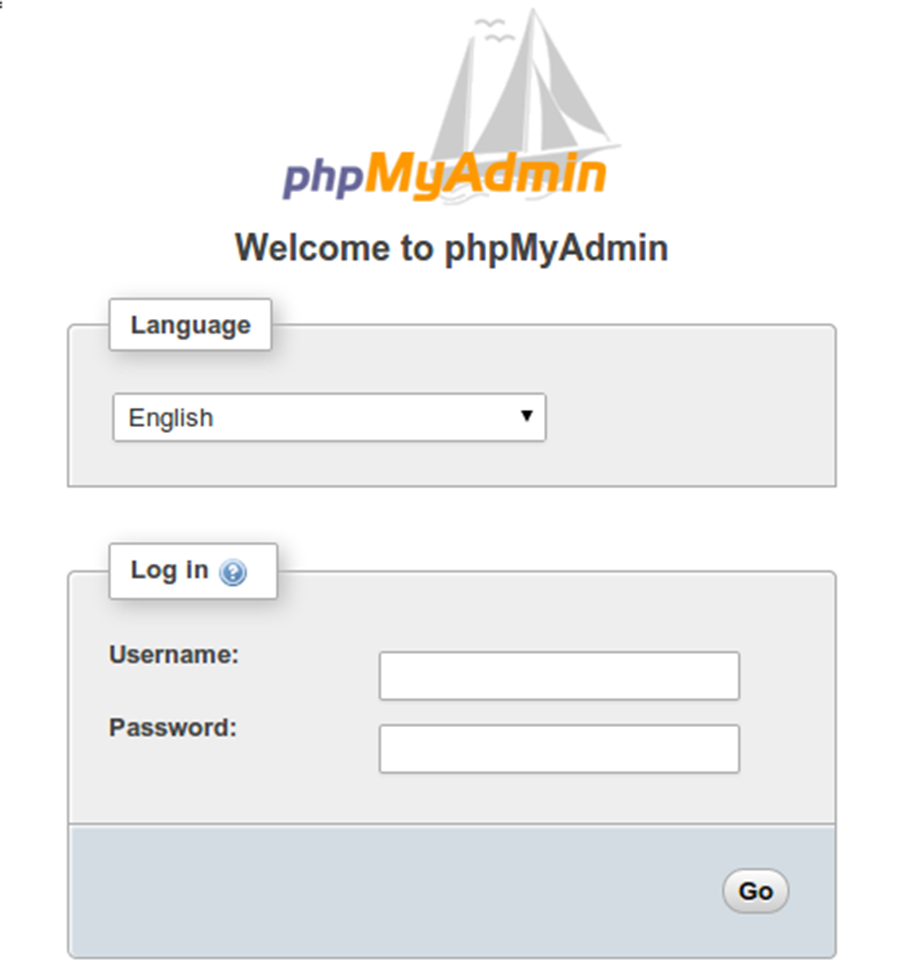
phpMyAdmin is a web-based client written in php for managing MySQL and MariaDB databases. It provides a user friendly web interface to access and manage your databases. To ease usage to a wide range of people, phpMyAdmin is being translated into 72 languages and supports both LTR and RTL languages.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo’ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step by step installation phpMyAdmin with Nginx on an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) server.
Install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Ubuntu
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade <strong> Step 2. Installing phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. </strong> Use this command to install phpmyadmin on Ubuntu 18.04: [php] sudo apt install phpmyadmin
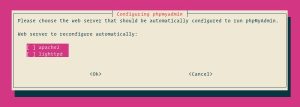
The installer will ask you to choose the web server that should be automatically configured to run phpMyAdmin. There is no option to choose Nginx, press TAB to select OK and then Enter. We’ll configure Nginx in the next section.
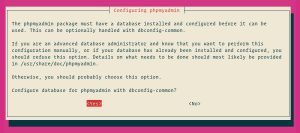
Next, the installer will ask you whether you want to use dbconfig-common tool to set up the database. Select Yes and hit Enter.
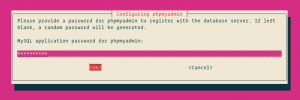
Enter a password for phpMyAdmin to register with the database, select OK and press Enter.
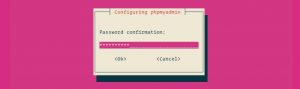
You will be prompted to confirm the password, enter the same password, select OK and press Enter.
Step 3. Configure Administrative MySQL.
Start by logging in to the MySQL server as the root user:
sudo mysql
From within the MySQL shell execute the following commands which will create a new administrative user and grant appropriate permissions:
CREATE USER 'padmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'change-with-your-secure-password';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'padmin'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Step 4. Configure Nginx to serve phpMyAdmin.
In Nginx, virtual host file can be found in etc/nginx/snippets directory. Let’s create a file called “phpmyadmin.conf”: sudo nano /etc/nginx/snippets/phpmyadmin.conf
Add the following content:
location /phpmyadmin {
root /usr/share/;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location ~ ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.php)$ {
try_files $uri =404;
root /usr/share/;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
}
location ~* ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.(jpg|jpeg|gif|css|png|js|ico|html|xml|txt))$ {
root /usr/share/;
}
}
Then, add the following line to each domain’s server block where you want to access phpMyAdmin using: domain.com/phpmyadmin:
include snippets/phpmyadmin.conf;
### /etc/nginx/conf.d/domain.com.conf
server {
# . . . other code
include snippets/phpMyAdmin.conf;
# . . . other code
}
Step 5. Finally, test phpMyAdmin.
Now open your browser and surf to http://youripaddress/phpMyAdmin and your phpmyadmin will ask you for user and password of your mysql installation, you can use root as user and the root mysql password, or any other mysql user/password.
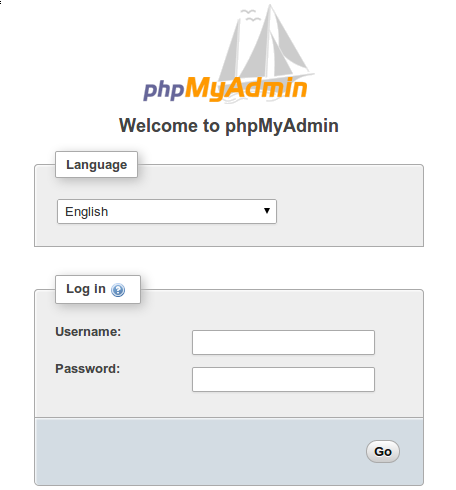
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed phpMyAdmin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official phpMyAdmin web site.