Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual weblog posts, as well as categories and other lists of weblog postings. A permalink is what another weblogger will use to link to your article (or section), or how you might send a link to your story in an e-mail message. The URL to each post should be permanent, and never change — hence permalink. In this tutorial, we will learn about WordPress SEO friendly URLs, and how you can customize your WordPress permalinks.
What is a SEO Friendly URL?
Before we go too deep into WordPress permalinks, it’s important that we define what is a SEO Friendly URL.
SEO Friendly URLs contain keywords that explain the article, and they’re easy to read by both humans and search engines. They also improve your chances to rank higher in search engines.
Example of a SEO friendly URL:
http://www.example.com/how-to-install-wordpress/
So what does a non-SEO friendly URL look like?
http://www.example.com/?p=10467
By default, WordPress now uses the post name in the URL which is the most SEO friendly URL structure.
So why do beginners still ask us for best permalink structure?
That’s because in the past, WordPress did not use pretty URLs also known as permalinks. The default used to be the non-SEO friendly example that we shared above.
This was changed in WordPress 4.2. If you recently installed WordPress, then your site URLs are SEO friendly.
You can easily verify your permalink settings in your WordPress admin area.
The Permalink Settings Page Explained
In WordPress, links are called Permalinks (short for permanent links). You’ll see the term permalink structure and URL structure being used interchangeably.
First thing you need to do is to visit the Permalinks settings page in your WordPress admin area.
Simply click on Settings link in the admin menu and then click on Permalinks. This will take you to a page that looks like this:
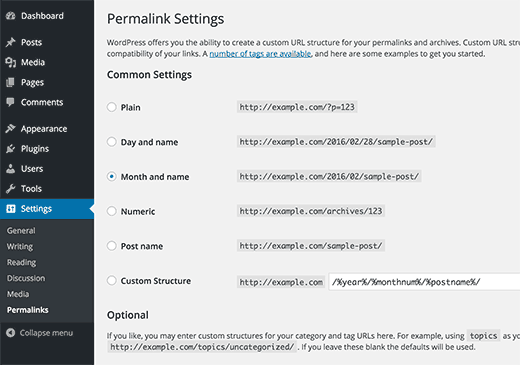
As you can see there are number of choices available.
- Plain
https://www.wpcademy.com/?p=123 - Day and name
https://www.wpcademy.com/2016/01/22/sample-post/ - Month and name
https://www.wpcademy.com/2016/01/sample-post/ - Numeric
https://www.wpcademy.com/archives/123 - Post name
https://www.wpcademy.com/sample-post/ - Custom Structure
Choose your own URL structure using available tags.
Let us explain these options a bit, and how useful they are for users and SEO.
The first option which is called plain used to be the default WordPress URL structure. This is not an SEO friendly option.
The day and name option is somewhat SEO friendly as it has the post name in it. However, with dates, the URL becomes too lengthy. But more importantly after some time your content seems outdated, even if you regularly update it. Similarly, the month and name option also runs the risk of being dated.
However if you’re a news publication, then you want to have the dates in your URL to show the recency and improve the user experience.
In our opinion, those two structures are only good for news sites. Business sites that are hoping to create ever-green content should avoid it.
Post name option is the most SEO friendly because it is short and pretty.
If you are running a larger publication, then you can use a custom structure that can also be SEO friendly.
At WPCademy, We use a custom permalink structure that adds a category name along with the post name in the URL. Because our site is large and contain thousands of articles, it suits us very well. You will see larger publications follow a similar URL structure.
In order to use a custom URL structure, you will need to add special tags in the custom structure box. For example, we use:
/%category%/%postname%/
Notice how each tag is wrapped between percent signs. Also notice the trailing slashes / before, after, and between the tags.
Creating Custom URL Structure with Available Tags
For the best results, we recommend using the options we mentioned above. You can copy the URL structure we use on WPCademy or choose the post name as your URL structure.
However, there are plenty of other combinations you can create using tags. Here is a list of tags that you can use to create your own custom URL structure:
- %year% – The year of the post, four digits, for example 2016.
- %monthnum% – Month of the year, for example 05
- %day% – Day of the month, for example 28
- %hour% – Hour of the day, for example 15
- %minute% – Minute of the hour, for example 43
- %second% – Second of the minute, for example 33
- %postname% – A sanitized version of the title of the post (post slug field on Edit Post/Page panel). For example, if your post title is This Is A Great Post! It would become this-is-a-great-post in the URL.
- %post_id% – The unique ID # of the post, for example 423
- %category% – A sanitized version of the category name (category slug field on New/Edit Category panel). Nested sub-categories appear as nested directories in the URI.
- %author% – A sanitized version of the author name.
Don’t forget to click on the save changes button after choosing your permalink structure.
As soon as you press the save changes button, WordPress will automatically update your site’s .htaccess file and your site will immediately start using the new URL structure.
Warning: Important Note for Established Sites
If your site has been running for more than 6 months, then please don’t change your permalink structure.
You don’t have to use the same structure that we used.
By changing your permalink structure on an established site, you will lose all of your social media share count and run the risk of losing your existing SEO ranking.
If you must change your permalink structure, then hire a professional, so they can setup proper redirects. You’ll still lose your social share counts on the pages.
There’s only one exception to this rule. If your site is using the plain URLs, then no matter how old it is, you should update the URL structure for better SEO. Yes, you will still lose social share counts, but the benefits far outweigh that.
We hope this tutorial helped you create a SEO friendly URL structure for your WordPress site.